1 - 图论入门
快速入门图论!本文介绍图的两个存储方式(邻接矩阵和邻接表),以及图的遍历方式。
图的存储
图分为有向图和无向图,只需考虑有向图的存储即可,因为无向图可看作双向的有向图。
邻接矩阵
对于稠密图,可以使用邻接矩阵来存储。g[a][b] = 1 表示一条有向边 a -> b,权值为 1.
邻接表
对于稀疏图,可用邻接表来存储。
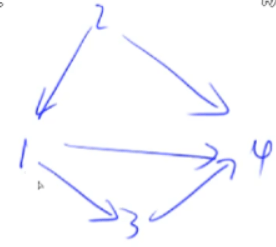
例如上图使用邻接表存储后,邻接表如下:
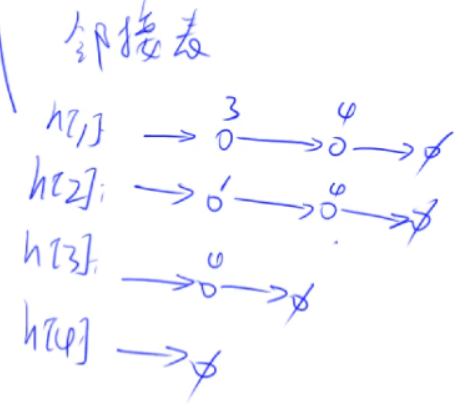
邻接表的代码实现如下(用数组实现链表):
struct Graph { // 用单链表存储节点i和它相连的节点j vector<int> h, e, ne; //vector<int> value;// 存放边的权 int idx; // 边的编号(总数) // 用头插法添加边a->b, /*权值为val*/ void add(int a, int b, /*int val*/) { e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; // value[idx] = val; h[a] = idx++; } Graph(int n) : h(n, -1), e(2 * n, 0), ne(2 * n, 0), idx(0) {} };
图的遍历
图的遍历和树的遍历差不多,但 图可能包含重边和自环:

为了让节点不被重复遍历,遍历框架要用一个 visited 数组进行辅助,如有需要,可用 path 数组来标记当前遍历经过哪些节点。
DFS
找一个起点,然后沿一条路走到底就行,然后回溯,直到所有点都遍历完。
797. 所有可能的路径 - 力扣(LeetCode)
可以使用 DFS,从节点 0 出发,找到节点 n-1 为止:
vector<vector<int>> paths; vector<int> path; void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& graph, int node) { // 找到了 if (node == graph.size() - 1) { paths.push_back(path); return; } // 遍历该点的所有相邻节点 for (int i = 0; i < graph[node].size(); ++i) { if(graph[node][i]) { path.push_back(graph[node][i]); dfs(graph, graph[node][i]); // 别忘了回溯 path.pop_back(); } } } vector<vector<int>> allPathsSourceTarget(vector<vector<int>>& graph) { // 从0开始 path.push_back(0); dfs(graph, 0); return paths; }
PS:这里使用邻接表存储图,i -> graph[i][j] 表示一条节点为 i, graph[i][j] 的有向边。
846. 树的重心 - AcWing 题库
假设每一个节点都是中心,删除该节点后,整个树便变成了若干连通块,其中:
- 通过 DFS 计算出该节点各个子树 (即各个子连通块),我们要这些子连通块节点和的最大值
- 非子树的一个连通块的数量可由总节点个数减去前面子连通块的个数总和得到。
最后我们取 遍历每个节点得到的两个连通块最大值 的最小值就行。参考代码如下:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; struct Graph { vector<int> h, e, ne, visited; int idx, n; void add(int a, int b) { e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx++; } Graph(int n) : h(n, -1), e(n * 2, 0), ne(n * 2, 0), visited(n, 0), idx(0) {} }; int ans = 100010, n; int dfs(Graph &graph, int u) { // 节点u已被访问 graph.visited[u] = 1; // 子连通块节点总和, 某子连通块节点和最大值 int subSum = 1, res = 0; // 遍历节点u所有边, 求出各子树节点和 for (int idx = graph.h[u]; idx != -1; idx = graph.ne[idx]) { int j = graph.e[idx]; if (!graph.visited[j]) { int subCnt = dfs(graph, j); res = max(subCnt, res); subSum += subCnt; } } // 每个节点得到的连通块最大值 res = max(n - subSum, res); // 找这些最大值的最小值 ans = min(res, ans); return subSum; } int main() { cin >> n; Graph graph(n + 5); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int a, b; cin >> a >> b; graph.add(a, b); graph.add(b, a); } // 从节点1开始 dfs(graph, 1); cout << ans; return 0; }
BFS
从起点开始,用 BFS 框架一层一层地找就行了。
847. 图中点的层次 - AcWing 题库
要求最短距离,可用 BFS。我们用一个 dist 数组记录点 i 到起点的距离,并进行 BFS,找到终点时返回即可。
参考代码如下:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> using namespace std; struct Graph { vector<int> h, e, ne, dist; int idx; void add(int a, int b) { e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx++; } Graph(int n, int m) : h(n + 5, -1), e(m + 5, 0), ne(m + 5, 0), dist(n + 5, -1), idx(0) {} }; int bfs(Graph& graph, int n) { queue<int> q; q.push(1); graph.dist[1] = 0; while (!q.empty()) { int cur = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int idx = graph.h[cur]; idx != -1; idx = graph.ne[idx]) { int next = graph.e[idx]; if (graph.dist[next] == -1) { graph.dist[next] = graph.dist[cur] + 1; q.push(next); } } } return graph.dist[n]; } int main() { int n, m; cin >> n >> m; Graph graph(n, m); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { int a, b; cin >> a >> b; graph.add(a, b); } cout << bfs(graph, n); }