1 - BFS入门
思想
把一些问题抽象成图,从一个点开始,向四周扩散,然后问你求最短路。当边权为1时,才能用BFS。BFS找到的路径一定是最短的,但代价就是空间复杂度可能比DFS大得多。
BFS的代码框架如下:
queue.push(初始状态)
while (队列不空)
{
取队头t
拓展队头t
}练习题
最短路问题
走迷宫
844. 走迷宫 - AcWing题库
可以从起点(0, 0)开始BFS,每往前走一步,就记录当前位置离起点的距离。这样BFS结束后,终点(n - 1, m - 1)的距离就是离起点的最短距离。
参考代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
vector<vector<int>> map(110, vector<int>(110, 0)), dist(110, vector<int>(110, -1));
int bfs()
{
// 初始状态
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({0, 0});
dist[0][0] = 0;
vector<pair<int, int>> dir = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};
// while队列不空
while (!q.empty())
{
// 取队头
auto [x, y] = q.front();
q.pop();
// 拓展队头
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
auto [dX, dY] = dir[i];
pair<int, int> next = {x + dX, y + dY};
if (next.first >= 0 && next.first < n &&
next.second >= 0 && next.second < m &&
map[next.first][next.second] == 0 &&
dist[next.first][next.second] == -1)
{
dist[next.first][next.second] = dist[x][y] + 1;
q.push(next);
}
}
}
return dist[n - 1][m - 1];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; ++j)
{
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
cout << bfs() << '\n';
}二叉树的最小深度
111. 二叉树的最小深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
和“最短路径”有关,可以用BFS。最开始将根节点和它的深度1入队,然后开始BFS循环,取队头元素,判断是否是叶子节点(左右子节点均为空),不是的话就入队子节点和它的深度。
参考代码如下:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
queue<pair<TreeNode*, int>> q;
q.push({root, 1});
while (!q.empty())
{
// 取队头
auto [cur, depth] = q.front();
q.pop();
// 验证是否是叶子节点
if (cur->left == nullptr && cur->right == nullptr)
return depth;
// 拓展队头
if (cur->left) q.push({cur->left, depth + 1});
if (cur->right) q.push({cur->right, depth + 1});
}
return 1;
}打开转盘锁
752. 打开转盘锁 - 力扣(LeetCode)
要求打开转盘锁的最小次数,可用BFS来解决,首先看看如何根据问题构造要层序遍历的多叉树:
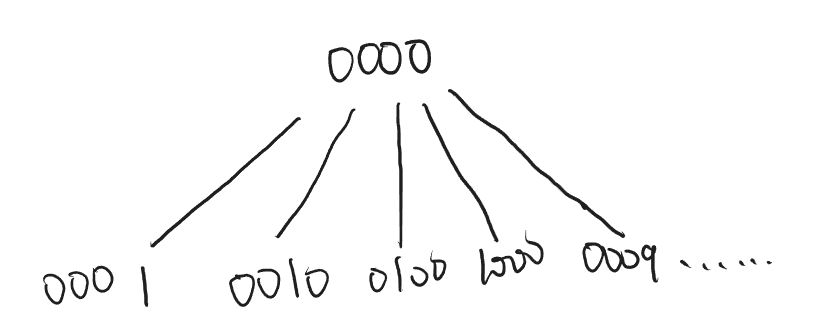
锁的每个状态可作为多叉树的节点,每次上/下拨视为状态转移。接下来,我们先把工具函数准备好:
// 将转盘锁从左往右第i为下拨
string plus(string str, int i)
{
if (str[i] == '9')
str[i] = '0';
else
++str[i];
return str;
}
string minus(string str, int i)
{
if (str[i] == '0')
str[i] = '9';
else
--str[i];
return str;
}然后就能写BFS框架了,需要注意的是,如果转出deadends里的数字,需要跳过本轮BFS。参考代码如下:
string plus(string str, int i)
{
if (str[i] == '9')
str[i] = '0';
else
++str[i];
return str;
}
string minus(string str, int i)
{
if (str[i] == '0')
str[i] = '9';
else
--str[i];
return str;
}
int openLock(vector<string>& deadends, string target) {
// 使用Hash存储deadends, 进行O(1)查询节省时间
unordered_set<string> visited;
visited.insert(deadends.begin(), deadends.end());
// 直接得出答案的情况
if (visited.count(target)) return -1;
if (target == "0000") return 0;
// BFS
queue<pair<string, int>> q;
q.push({"0000", 0});
while (!q.empty())
{
// 取队头
auto [cur, ans] = q.front();
q.pop();
// 验证是否是答案
if (cur == target)
return ans;
// 转到deadend里的数字就放弃BFS
if (visited.count(cur))
continue;
// 拓展队头
visited.insert(cur);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
string tmp = plus(cur, i);
if (!visited.count(tmp))
q.push({tmp, ans + 1});
tmp = minus(cur, i);
if (!visited.count(tmp))
q.push({tmp, ans + 1});
}
}
return -1;
}八数码
845. 八数码 - AcWing题库
和上面的的开锁问题同理,但这里有个难点,就是如何用一行字符串存储3x3棋盘:
- 首先找到目标字符在字符串中的索引。
- 在3x3棋盘中,x = 索引 / 3,y = 索引 % 3
- 索引 = x * 3 + y
参考代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
string start = "", target = "12345678x";
unordered_map<string, int> dist;
queue<string> q;
vector<pair<int, int>> dir = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
int main()
{
char ch;
while (cin >> ch)
start += ch;
// BFS
q.push(start);
dist[start] = 0;
while (!q.empty())
{
string cur = q.front();
q.pop();
int dis = dist[cur];
if (cur == target)
{
cout << dis;
return 0;
}
// 拓展队头: 让x上下左右四个方向分别与x交换
int idx = cur.find('x');
int x = idx / 3, y = idx % 3;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
auto [dx, dy] = dir[i];
int a = x + dx, b = y + dy;
if (a >= 0 && a < 3 && b >= 0 && b < 3)
{
swap(cur[idx], cur[a * 3 + b]);
if (!dist.count(cur))
{
dist[cur] = dis + 1;
q.push(cur);
}
swap(cur[idx], cur[a * 3 + b]);
}
}
}
cout << -1;
}其他
填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 - 力扣(LeetCode)
117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
是一道经典的二叉树的层序遍历题,应使用BFS。每次通过层序遍历,就能得到一层的二叉树节点,我们只需在用当层节点拓展下层节点的同时,将当层节点用链表连接起来就好了。
参考代码如下:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
vector<Node*> curLevel;
curLevel.push_back(root);
while (!curLevel.empty())
{
// 拓展下层所有节点的同时, 将当层节点连起来
vector<Node*> nextLevel;
for (int i = 0; i < curLevel.size(); ++i)
{
// 连接当层节点
if (i)
curLevel[i - 1]->next = curLevel[i];
// 拓展下层节点
if (curLevel[i]->left)
nextLevel.push_back(curLevel[i]->left);
if (curLevel[i]->right)
nextLevel.push_back(curLevel[i]->right);
}
curLevel = nextLevel;
}
return root;
}参考资料
- 《labuladong的算法笔记》
- 算法基础课 - AcWing